[NLP] Attention is all you need
With attention mechanism described here, this model uses attention, not other mechanisms like RNN.
Hyperparameters
There are several hyperparameters that are to be used to explain the model.
\[d_{model} = 512\]$d_{model}$ is the dimension of the embedding vector. For the values to be forwarded, the dimension stays the same.
\[num\,layers = 6\]The number of layers for the encoder and decoder.
\[num\,heads = 8\]This is the number of processes that are used in parallel.
\[d_{ff} = 2048\]This is the size of hidden layers for the feed-forward neural network in the transformer.
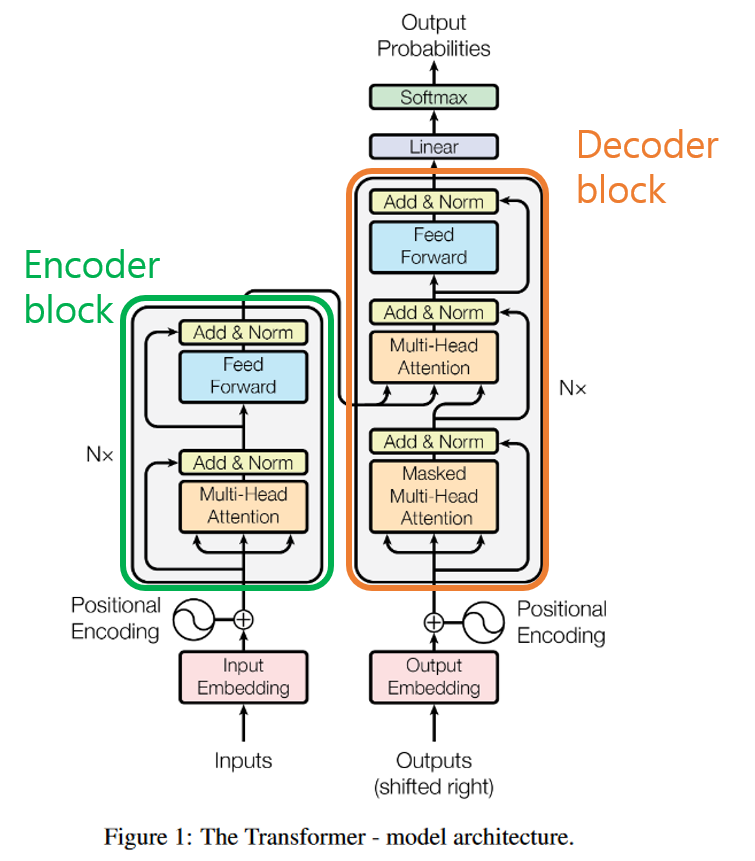
Transformer
This is the visual interpretation of the transformer model.
This is the basic interpretation, with input and output shown. <sos> is indicating the start, and <eos> is indicating the end of the sentence for the prediction.
The overall process is shown in the following diagram.
Positional Encoding
RNN was advantageous in natural language processing for having positional information. As Transformer does not receive the input of words sequentially, positional encoding is done on the input.

With the embedding vectors for each word, positional encoding is added. For providing positional values, there are two functions used:
\(PE_{(pos, 2i)} = sin(pos / 10000)^{2d/d_{model}}\) \(PE_{(pos, 2i + 1)} = cos(pos / 10000)^{2i/d_{model}}\)
This is the diagram for better understanding. When the index is even, sin function is used. If the index is odd, cosine function is used.
Attentions used
There are three types of attention mechanisms used.
- Encoder Self-Attention
Self-attention is the processing of attention mechanism on oneself. This means that query, keys and values are from the same type of cell.
Encoder Self-Attention can be interpreted as using Q, K and V as the word vectors of the input.
For this step, Q, K, and V vectors are to be retrieved from the word vectors. The words have dimensions less than $d_{model}$.
The number of dimensions is decided by $num\, heads$. Here, the size is 64 for dividing $d_{model}$ with $num \, heads$.
Each weight matrix has size of $d_{model} * (d_{model} / num \, heads)$. For each weight matrix, the word vector is multiplied to get Q, K, and V vectors.
After getting the vectors, attention score is calculated with scaled dot-product attention. The scaling is done with softmax function executed on each attention score calculated using $q * k / \sqrt{d_k}$.
The overall process is seen through the image above.
Multi-head Attention
With the parallel processing, the efficiency increases with the model.
This is the visual interpretation. The values for weight matrices are different for each attention head.
This will be further explained with another post.
Padding Mask
Under scaled dot-product attention, masking is done. This is done to do not consider the words that are not present at the decoded time.
Position-wise Feed-Forward Neural Network
There is a neural network, with the number of layers $d_{ff}$. The equation is as follows:
\[FFNN(x) = MAX(0, xW_1, b_1)W_2 + b_2\]$x$ is the result of multi-head attention (seq_len, $d_model$). $W_1$ has size of ($d_{model}, d_{ff}$), and $W_2$ has size of ($d_{ff}, d_{model}$). Within the encoder, the parameters remain the same. However, for other encoders, the values change.
Residual Connection & Layer Normalization
Both are applied for Multi-head Self-Attention and FFNN. Residual connection refers to adding the input and output of certain function to create a new function.
This is residual connection for Multi-head Attention.
After such a process, layer normalization is done.
Each row is normalized for the size of $d_{model}$
After the transformation, the output is as follows:
\[ln_i = \gamma\hat{x}_i + \beta = LayerNorm(x)\]where $\gamma$ is initialized with 1 and $\beta$ is initialized with 0.
Decoder
For decoders, the sentence matrix after embedding and positional encoding is provided as input.
The problem is that the input is with the whole sentence. This forces decoders to utilize look-ahead mask. This is done at the first sub-layer of decoders.
The second sub-layer, multi-head attention, transfers padding mask., instead of look-ahead mask.
For encoder-decoder attention, this is not a self-attention described previously. Q matrix is from the decoder, but K and V are from the encoder.
Conclusion
This model is still in use for different language models, and this is set as standard for such a process. Understanding and implementing transformer can be a great exercise for the further knowledge acknowledgement.










